Introduction
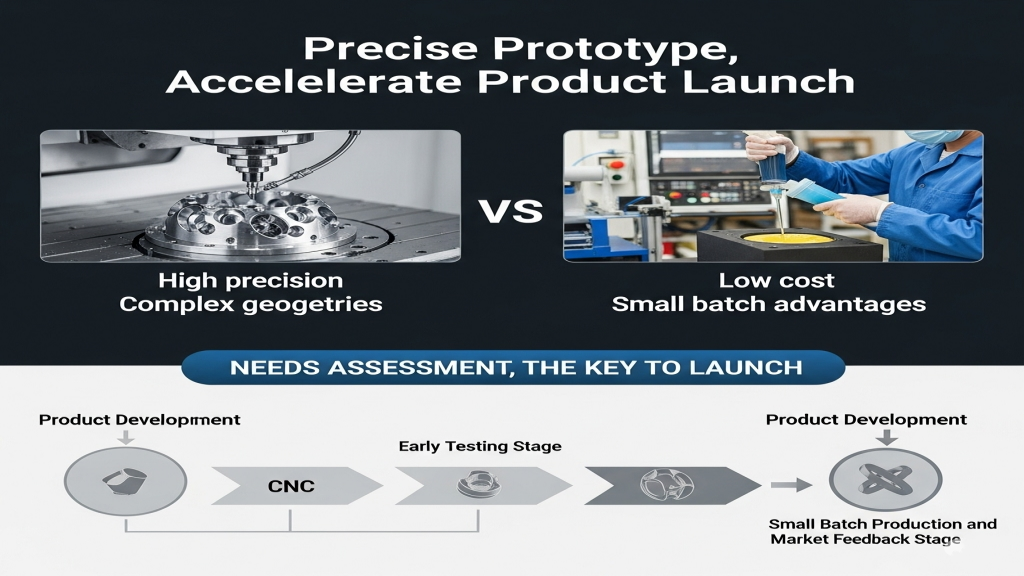
CNC prototyping enables complex geometry quickly and suits early-stage testing. Rapid molds, while less precise, are ideal for small-volume production and market feedback. Each approach has a clear role in different development phases.
Choosing the right method affects not only cost but also lead time and iteration cycles. Accurate need evaluation is key to winning the product launch battle.
Is CNC faster for prototyping?
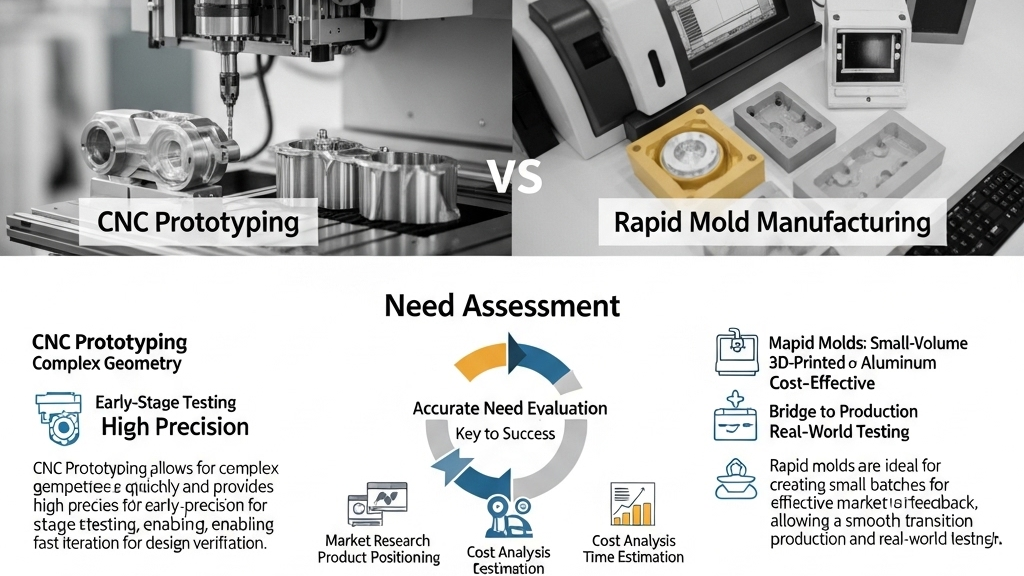
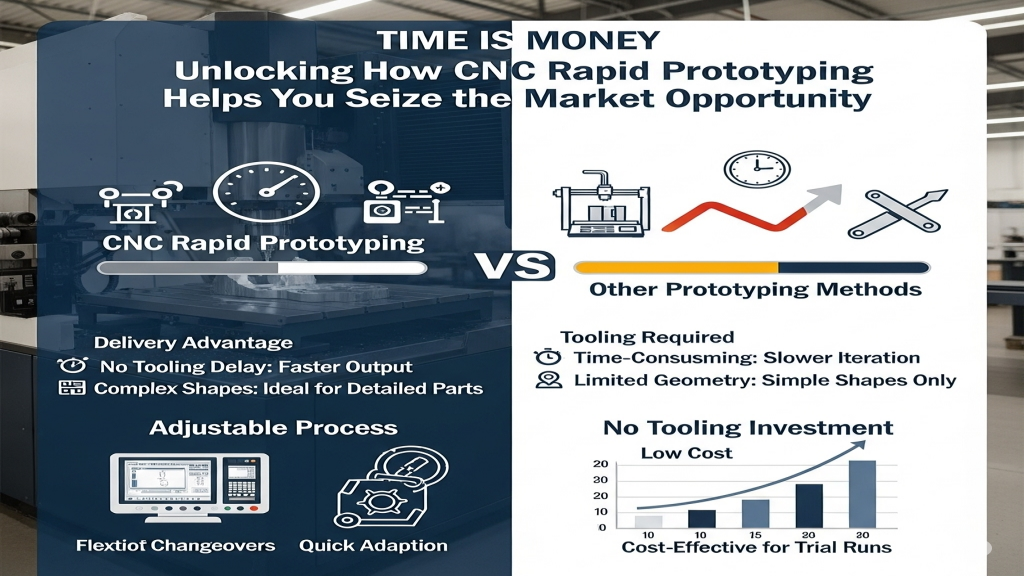
Early-stage projects demand speed to gain market edge. CNC samples can be quickly made for structural and appearance validation. For time-sensitive projects, CNC is almost the “only answer.”
- Delivery Advantage: Understand CNC Rapid Prototyping – no tooling delay, faster output.
- Handles Complex Shapes: Ideal for curved, angled, or detailed parts.
- Adjustable Process: CNC Machine Setup Tips – flexible changeovers.
- No Tooling Investment: Great for single-piece or trial runs at low cost.
CNC is your go-to solution for rapid validation without mold commitment.
Is rapid tooling more cost-effective?
Rapid molds offer lower costs and shorter cycles, making them perfect for small-scale injection trials. Compared to CNC, it’s closer to real production conditions.
- Batch Efficiency: Rapid Tooling Guide – multiple parts in one mold cycle.
- Tooling Cost Advantage: Simple structures and affordable materials.
- Material Consistency: Real Injection Resin – accurate simulation of production conditions.
- Ideal for Market Testing: Efficient for low-risk pre-launch feedback.
Rapid mold lets you test the market affordably before full-scale production.
How do they differ in precision?
CNC excels in precision validation, while rapid molds offer consistency in repeat batches. Each method delivers value based on your goal.
- Precision Edge: CNC Tolerance Reference – within ±0.05mm.
- Surface Control: Ideal for functional and visual prototypes.
- Molded Accuracy: Injection Mold Tolerance – consistent in repeat use.
- Risk Management: CNC is more adaptable in early design changes.
Precision matters, but only when aligned with your specific needs.
Which Phase Fits Best?
|
Criteria |
CNC Prototype |
Rapid Mold |
Suggested Use |
Cost Investment |
| Lead Time | Fast | Medium | Fast Validation | Low |
| Batch Ability | Low | Medium | Market Trial | Moderate |
| Cost Efficiency | Material + Time | Tooling Expense | Phase-Based | Stepwise |
| Accuracy | High (Adjustable) | Medium (Fixed) | Fine Detail Fit | Basic Structure |
Material Flexibility
CNC supports a wide range of plastics and metals, ideal for structural and strength validation. Rapid molds align with actual injection-grade plastics. Material selection directly impacts product performance and suitability.
1.Diverse Options: CNC can use PC, POM, PA, etc.
2.Realistic Structure: Rapid molds reproduce actual mass production results.
3.Trial-Friendly: CNC allows early-stage testing of different resins.
4.Function-Driven: Final use dictates material and molding choice.
Conclusion
CNC prototyping is ideal for initial validation and rapid turnaround, while rapid molds support pre-production testing and small-volume output. The choice hinges on correctly identifying your project’s development stage. Combining both can reduce uncertainty, shorten lead time, and optimize cost.Switching methods strategically boosts development efficiency.
For expert assistance in implementing solutions for your production needs, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you scale up your manufacturing with precision and efficiency!
Post time: Jul-24-2025
