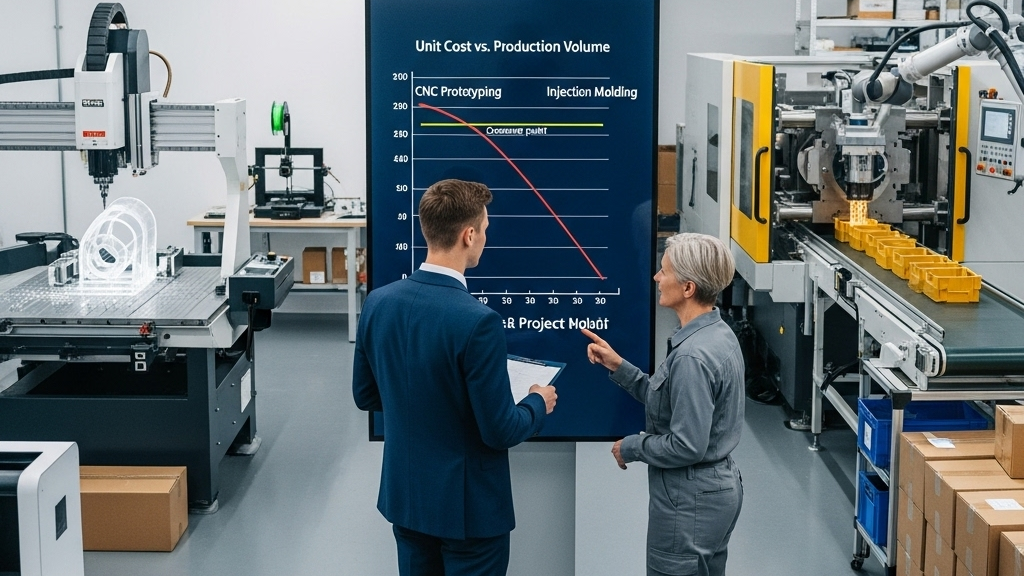

The cost curves of CNC acrylic machining and injection molding are not linear—they vary dramatically with production volume. CNC avoids mold costs and enables rapid design validation. Controlling cash flow during prototyping is crucial for startups.
As volumes increase, injection molding benefits from amortized tooling, material efficiency, and cycle time reduction. Identifying the crossover point is key to winning price-sensitive markets.
Is CNC more cost-effective for small batches?
Within the 1–500 pcs range, CNC avoids expensive tooling, and cost mainly depends on machine time and raw material. Auto tool changers and 5-axis machining boost acrylic cutting efficiency. For design verification, CNC can deliver samples within a day.
- Rapid Iteration: Design tweaks can start with the first part.
- Instant Quoting: Transparent and fast pricing.
- Cloud Manufacturing: Distributed production shortens lead times.
- Flexible Fixtures: Supports variant testing without extra jigs.
When does injection molding surpass CNC in cost?
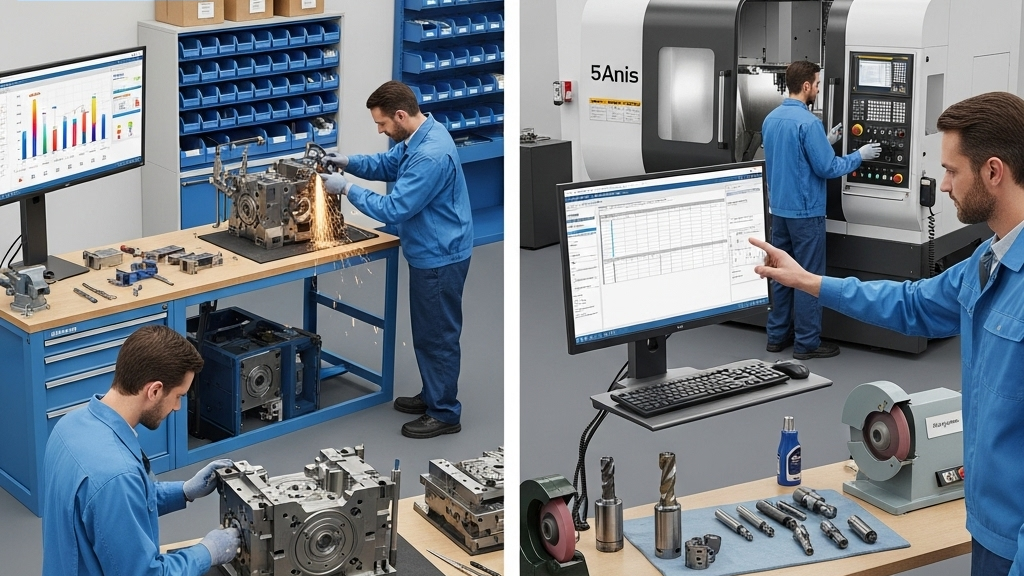

When batch sizes exceed around 2,000 pieces, mold amortization sharply reduces unit costs. Faster cycles and scrap recovery enhance economics. Tooling cost becomes the pivot point of the cost curve.
- Amortization Effect: Mold cost drops below $0.20/unit.
- Automation: Robotic demolding saves labor.
- Lean Scheduling: MES systems cut idle time.
- Bulk Material Pricing: Ton-level orders lower resin cost by 5–8%.
Where do long-term maintenance costs show up?

Injection molds require regular polishing or chrome plating to prevent acrylic wear, adding long-term cost. CNC uses tool life management to allocate wear. Neglected maintenance can cause a secondary cost surge.
- Mold Refurbishing: Re-plating extends life up to 500K cycles.
- Spare Parts: Backup inserts avoid downtime.
- Smart Monitoring: Sensors detect early wear.
- Tooling Control: Standardized tools reduce 20% on consumables.
Cost Stage Comparison Table
|
Stage |
Unit Cost (USD) |
Mold Fee (USD) |
Lead Time |
Batch Size |
| CNC Small Batch | 18.00 | 0 | 1–3 days | 1–500 |
| CNC Mid Batch | 12.50 | 0 | 3–5 days | 500–2,000 |
| Injection Low Volume | 7.80 | 4,500 | 10–14 days | 2,000–10,000 |
| Injection High Volume | 1.10 | 4,500 | 15–30 days | 10,000+ |
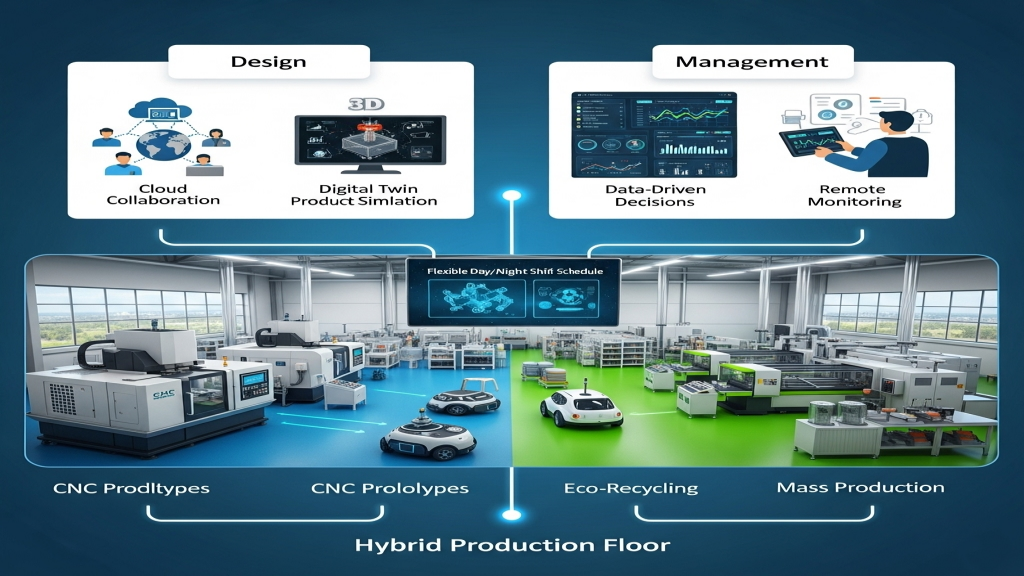
Expansion
Shorter product lifecycles push companies to prioritize speed-to-market. Cloud-based collaboration compresses the design-to-delivery cycle. Mastering hybrid production lets you stay competitive on both price and speed.
1.Hybrid Production: Start with CNC, scale with molding.
2.Digital Twin: Simulate and plan cost curve transitions.
3.Flexible Scheduling: Night shifts lower electricity bills.
4.Eco Recycling: Reuse acrylic waste for sustainability.
Conclusion
The cost crossover between CNC and injection molding is dynamic and context-sensitive. Companies should continuously evaluate the triangle of tooling, volume, and delivery. Switching processes at the right volume point can reduce total manufacturing cost by over 30%. With smart monitoring and scheduled maintenance, you can maintain stable profit margins as you scale.
For expert assistance in implementing for your production needs, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you scale up your manufacturing with precision and efficiency!
Post time: Jun-18-2025
