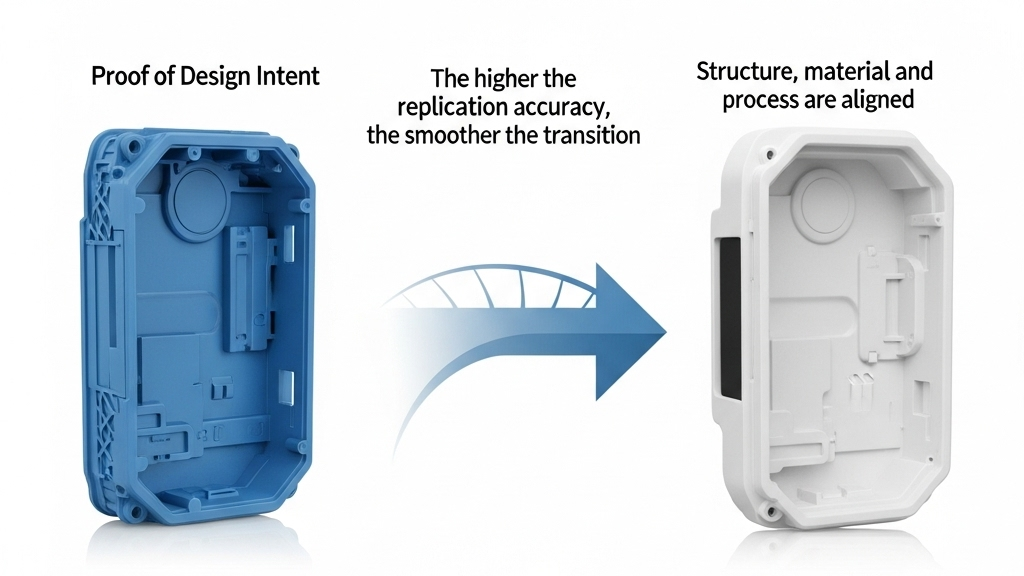
From initial concept to mass production, ABS prototypes play a vital role in evaluating appearance, structure, and functionality. They are not only the proof of design intent but also a critical bridge to production. The higher the replication accuracy, the smoother the transition from design validation to production.
In injection molding projects, replication accuracy and detail fidelity directly affect product consistency and process stability. Only when structure, material, and process are aligned can a prototype be fully replicated into a molded product.
How consistent are ABS prototypes with molded parts in structural precision?

Structural design determines whether a prototype can be successfully transitioned into an injection-molded part. Wall thickness distribution, rib layout, and draft angles must be finely tuned at the prototype stage. Structural deviations are often the root cause of failed replication.
- Structural Deviation Correction: Reduces warpage during molding.
- Wall Thickness Uniformity: Avoids shrinkage-related deformation.
- Draft Angle Matching: Ensure sufficient draft in both prototype and mold.
- Rib Layout Optimization: Manage shrinkage zones in advance.
Can ABS prototypes accurately reflect functional strength?

ABS prototypes are often used for functionality testing, but their mechanical properties still differ from molded parts. Load direction, stress points, and assembly strength must be reevaluated through mold flow analysis. Prototypes can only approximate the functional strength of molded parts when structurally sound.
- Structural Simulation: Predicts performance during testing.
- Connection Point Design: Ensures alignment from prototype to final product.
- Assembly Strength Calibration: Tests stress behavior in prototype joints.
- Functional Load Testing: Analyzes fatigue under repeated stress.
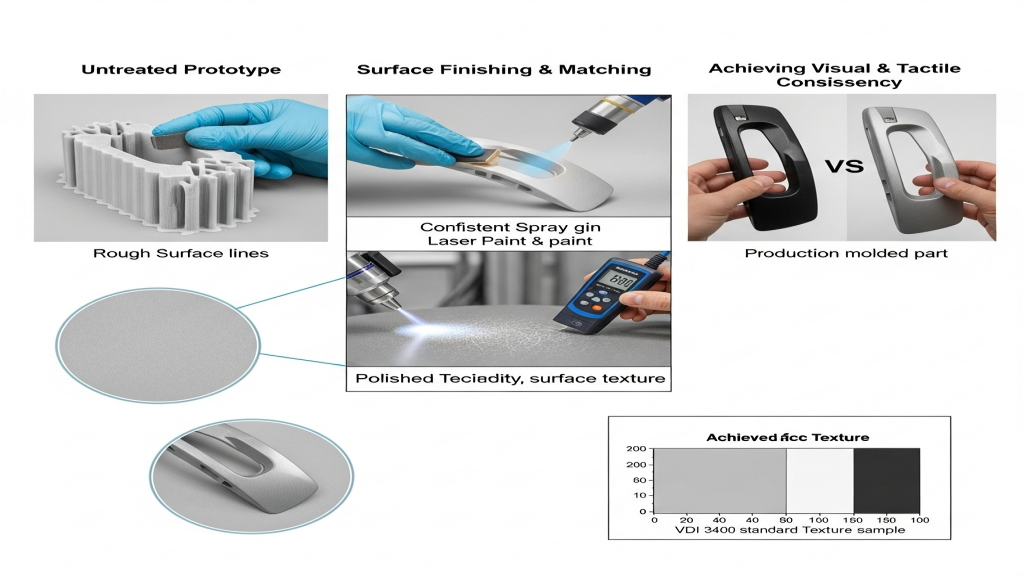
Can ABS prototype surface finishing match molded parts?

ABS prototypes, often made by 3D printing or CNC, cannot directly match the surface smoothness of molded parts. Without post-processing like spraying or polishing, visual and tactile deviations appear. Molded textures should be simulated and verified during the prototype stage.
- Texture Simulation: Ensures visual consistency.
- Spray Coating Comparison: Match color and gloss after painting.
- Polishing and Sanding: Improve shine consistency in prototype.
- Texture Standards Matching: Refer to VDI3400 or MT texture specs.
Differences in Fit Accuracy Between ABS Prototypes and Molded Parts
|
Item |
Prototype Fit |
Molded Fit |
Error Risk |
Impact Level |
Correction Strategy |
Mass Replicable |
| Wall Thickness | Medium | High | Moderate | High | Add control points | Yes |
| Surface Finish | Medium | High | High | Medium | Improve mold polish | Yes |
| Functional Strength | Medium | High | Moderate | High | Optimize rib structure | Yes |
| Detail Reproducibility | Low | High | High | High | Enhance model accuracy | No (Needs optimization) |
How do ABS prototypes help evaluate mass production feasibility?
In product development, ABS prototypes are essential for risk assessment before mold investment. They allow designers to anticipate potential issues in structure, functionality, and manufacturability. High-fidelity prototypes help accelerate the transition from design to tooling.
1.Faster Iteration Cycles: Catch design flaws early and reduce revisions.
2.Assembly Verification: Detect misalignments during physical assembly.
3.Functional Scenario Testing: Simulate product use under real conditions.
4.Lower Production Risks: Minimize tooling trial failures through early discovery.
Conclusion
ABS prototypes serve as a technical bridge between creative concepts and molded products. What they replicate goes beyond shape—it includes feasibility, functionality, and manufacturability evaluation. Only through deep analysis of prototype performance can we truly shorten the path to mass production.
For expert assistance in implementing for your production needs, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you scale up your manufacturing with precision and efficiency!
Post time: Jun-30-2025
