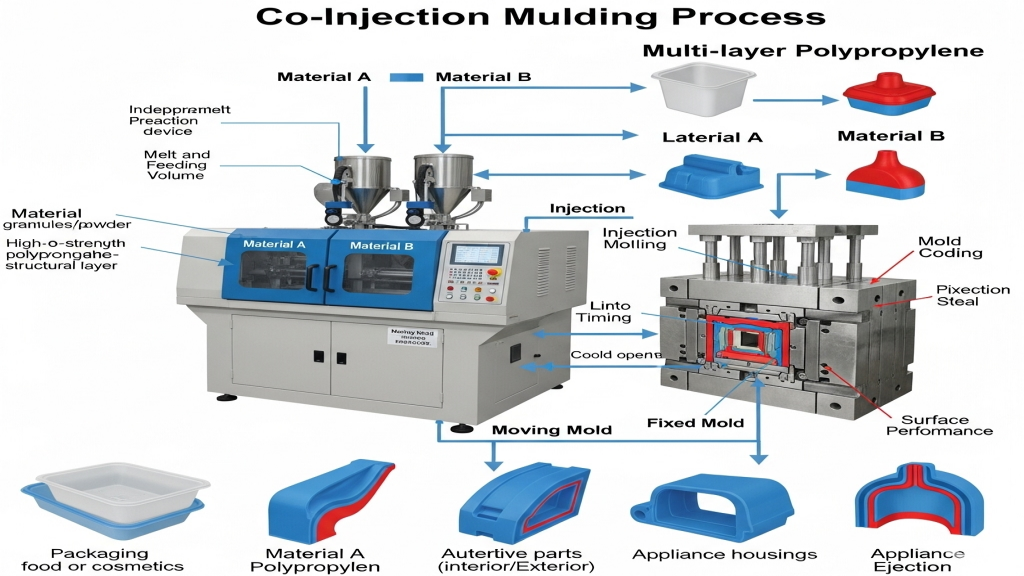
Co-injection molding is becoming a key technology for producing multi-layer polypropylene structures, widely used in packaging, automotive, and home appliances. This integrated process enables functional enhancement and market competitiveness.
This one-step multilayer process significantly reduces both cost and cycle time.
With growing demand for lightweight and high-performance plastic parts, co-injection molding offers strong advantages in bonding control and material compatibility. Its seamless layer transition ensures mechanical integrity and durability.
How Does Co-Injection Molding Create Multi-Layer Polypropylene?
Co-injection injects different polypropylene layers into the cavity simultaneously through separate feed ports. Each layer can be tailored with functions like UV resistance or oxygen barrier.Dynamic fusion of melts inside the mold ensures uniform distribution and interfacial strength.
- Process Path Optimization: Mold flow design determines final quality.
- Material Compatibility: Melt flow indexes must be closely matched.
- Design Flexibility: Enables 3–5+ layer complex structures.
- Precision Control: Temperature, pressure, and speed ensure consistent layers.
How to Ensure Bonding Strength Between Layers?
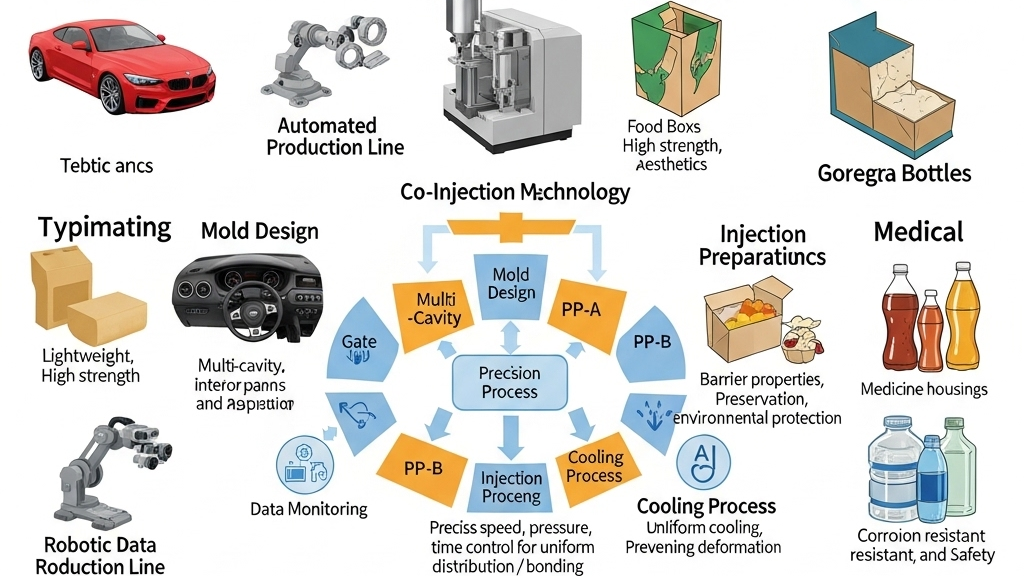
Bonding quality between layers is critical in multi-layer polypropylene structures. It is enhanced via melt temperature control, interface agents, and gate angle design.Interface fusion directly determines structure reliability and product lifespan.
- Interface Activation: Enhances molecular entanglement.
- Optimized Parameters: Balanced pressure and cooling improve adhesion.
- Accurate Material Selection: Layer functions dictate material pairing.
- Mold Design Reinforcement: Precise flow channels ensure close bonding.
What Are the Applications of Multi-Layer Polypropylene?
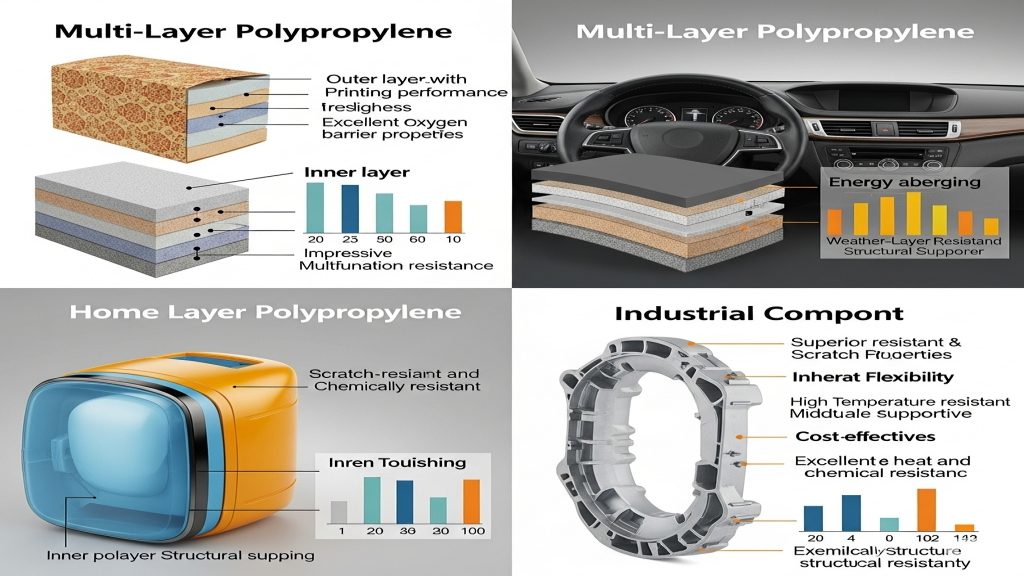
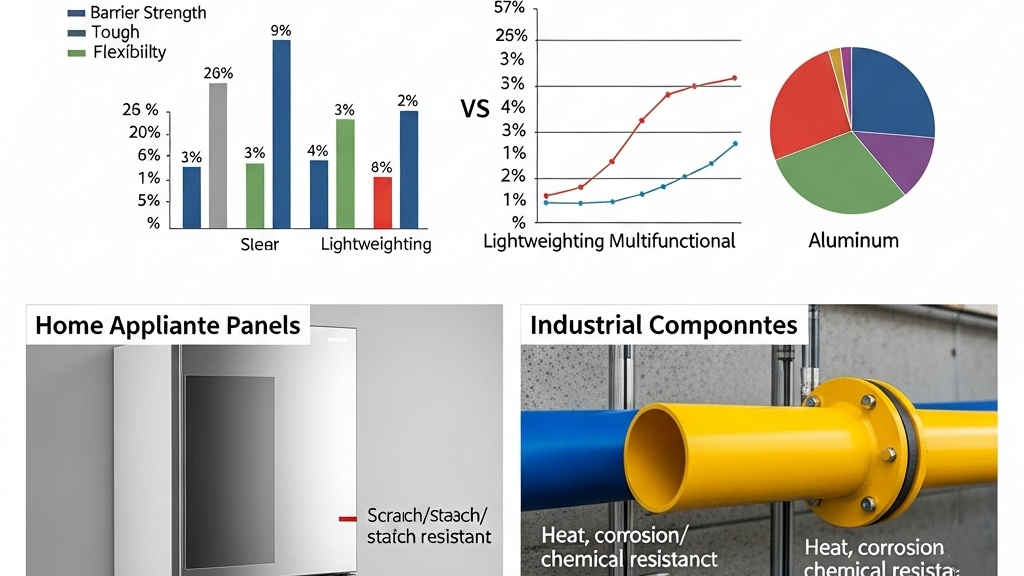
Multi-layer polypropylene is used in food films, automotive dashboards, and appliance housings. Its combined properties include barrier strength, toughness, and flexibility.It delivers both lightweight construction and multifunctionality, increasing product value.
- Food Packaging: Layers enhance preservation and barrier performance.
- Automotive Lightweighting: Replaces metal with lower weight and cost.
- Home Appliance Panels: Adds aesthetics and strength.
- Industrial Components: Suits complex, heat-resistant applications.
Process Comparison Table
|
Process Type |
Max Layers |
Bond Strength |
Equipment Needs |
Mold Complexity |
Cost Control |
Material Flexibility |
Application Scope |
| Single Injection | 1 | Not required | Low | Simple | High | Low | General Use |
| Multi-Shot Molding | 2–3 | Moderate | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium | Custom Products |
| Co-Injection | 3–7 | High | High | High | Optimal | High | High Performance |
| Hybrid Molding | Variable | Adjustable | High | High | Medium | High | Functional Parts |
Technology Extensions
As materials evolve, co-injection is pushing forward with more layers, functional polymers, and microspheres. These innovations improve insulation, damping, and fire resistance.Co-injection’s configurability makes it ready for future high-performance demands.
1.Microstructural Design: Enables miniaturization for 3C devices.
2.Smart Material Fusion: Blending polypropylene with barrier resins.
3.Eco-Layer Integration: Supports biodegradable outer layers.
4.Durability Enhancements: Applied in long-life industrial components.
Conclusion
Co-injection molding is a core technique for achieving multi-layer polypropylene structures, advancing functionality and smart manufacturing. From mold design to raw material precision, it drives high-value production lines.The technology will play a bigger role in automotive, packaging, and medical industries in the near future.
For expert assistance in implementing for your production needs, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you scale up your manufacturing with precision and efficiency!
Post time: Jun-04-2025
