
Fiber orientation in black polypropylene during injection molding often leads to visual and structural defects. Optimizing process parameters is essential to improve the one-shot molding quality. Optimizing process parameters is the key step to solving fiber orientation problems.
We control flow, mold design, and material preprocessing to reduce fiber alignment along the flow direction. This improves both the surface finish and structural consistency. Systematic control during molding directly impacts orientation control levels.
How to reduce appearance issues caused by fiber orientation?
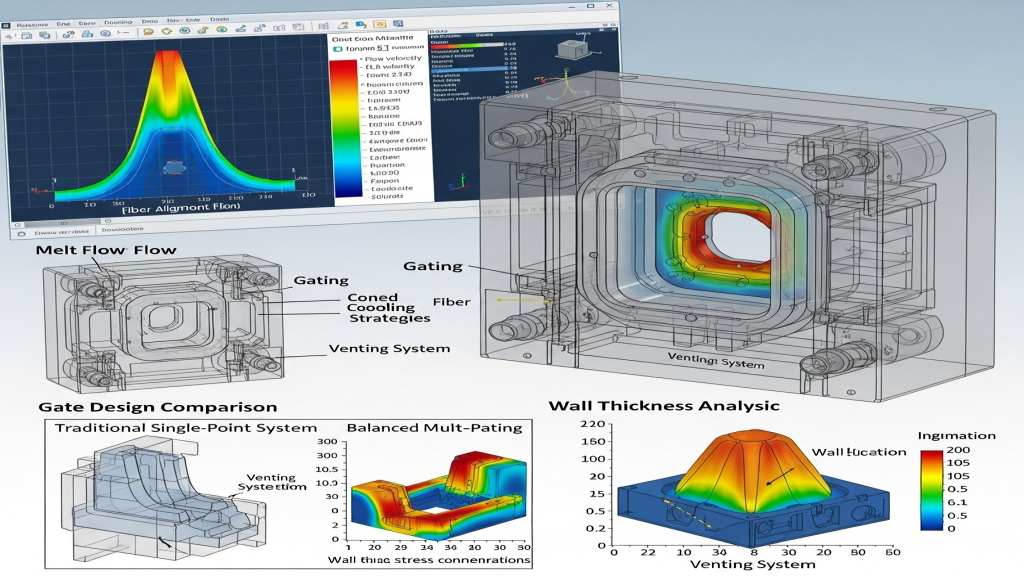
Fiber orientation causes gloss variation and streaks on the surface, affecting product aesthetics and consistency. Adjusting injection speed, mold temperature, and filler strategies helps relieve these issues.Controlling melt flow behavior in the cavity is crucial to avoid defects.
- Mold temperature optimization: Higher mold temps promote random fiber distribution.
- Lower injection speed: Slower flow reduces alignment tendency.
- Optimized gate design: Expands melt spread, reducing directional flow.
- Use of anti-orientation agents: Stabilizes fiber behavior under shear.
How do injection parameters affect fiber distribution?
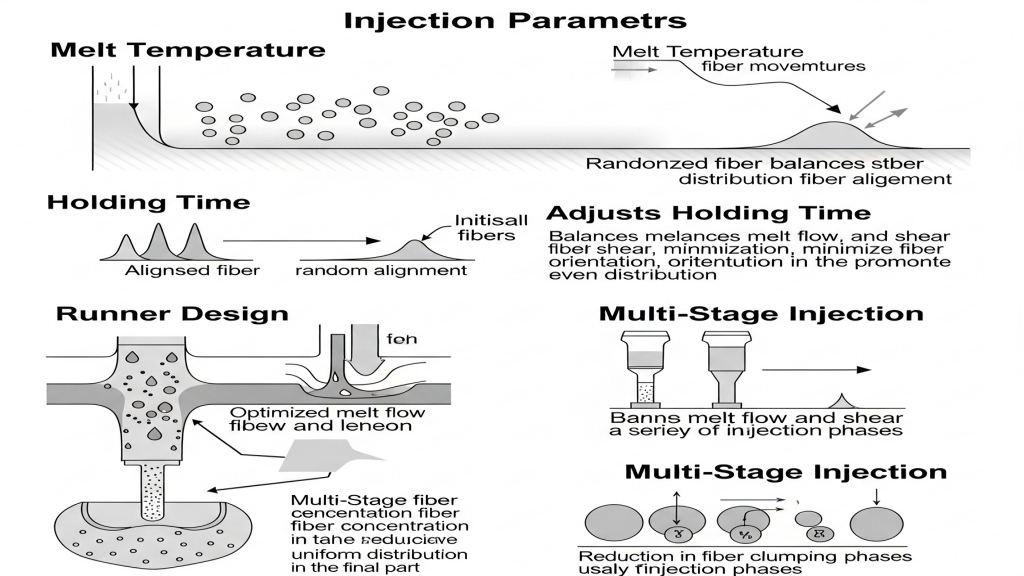
Temperature, pressure, and holding time influence fiber alignment in the melt. A well-defined process window reduces orientation induced by flow.A well-designed process window ensures uniform fiber distribution.
- Raise melt temperature: Helps fibers move more randomly.
- Adjust holding time: Balances flow-induced stress.
- Optimize runner design: Balances melt flow and shear.
- Multi-stage injection: Prevents fiber concentration in specific zones.
How can mold design reduce fiber orientation?
Mold structure affects flow, shear, and cooling—key elements influencing fiber behavior. Modifying gating and partition structures reduces directional accumulation. Mold design is a crucial part of fiber orientation control.
- Balanced gate location: Avoids unidirectional melt flow.
- Zoned cooling design: Cools different areas differently.
- Reduce wall thickness variance: Minimizes directional flow.
- Improve venting system: Lowers shear stress caused by trapped air.
Fiber Orientation Control
|
Parameter |
Influencing Factor |
Effect |
Recommended Range |
| Mold Temperature | Cooling Rate | Reduces alignment | 60–90°C |
| Injection Speed | Shear Rate | Slows fiber order | 20–40mm/s |
| Melt Temperature | Flow Characteristics | Enhances dispersion | 210–240°C |
| Holding Time | Stability | Reduces stress | 3–8 seconds |
How Design & Materials Work Together
Adding elastic particles or anti-orientation fillers weakens fiber alignment. Modular mold design minimizes unidirectional zones. Material and mold synergy ensures top performance in black PP parts.
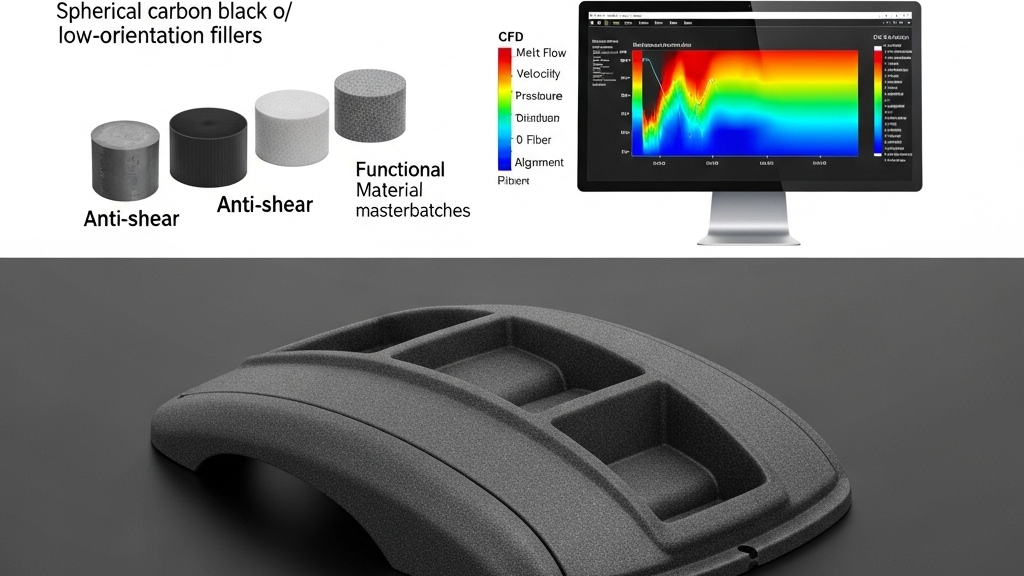
1.Material optimization: Use spherical carbon black or low-orientation fillers.
2.Modular design: Enhances flow uniformity.
3.Functional masterbatches: Improve shear resistance.
4.Use of CFD: Predicts and adjusts molding flow.
Conclusion
Reducing fiber orientation in black PP injection molding requires coordinated efforts across parameters, mold design, and materials.Each small optimization can dramatically improve part quality and consistency.With material innovations advancing, orientation defects will become even more manageable, enabling reliable one-shot production.
For expert assistance in implementing for your production needs, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you scale up your manufacturing with precision and efficiency!
Post time: Jun-05-2025
