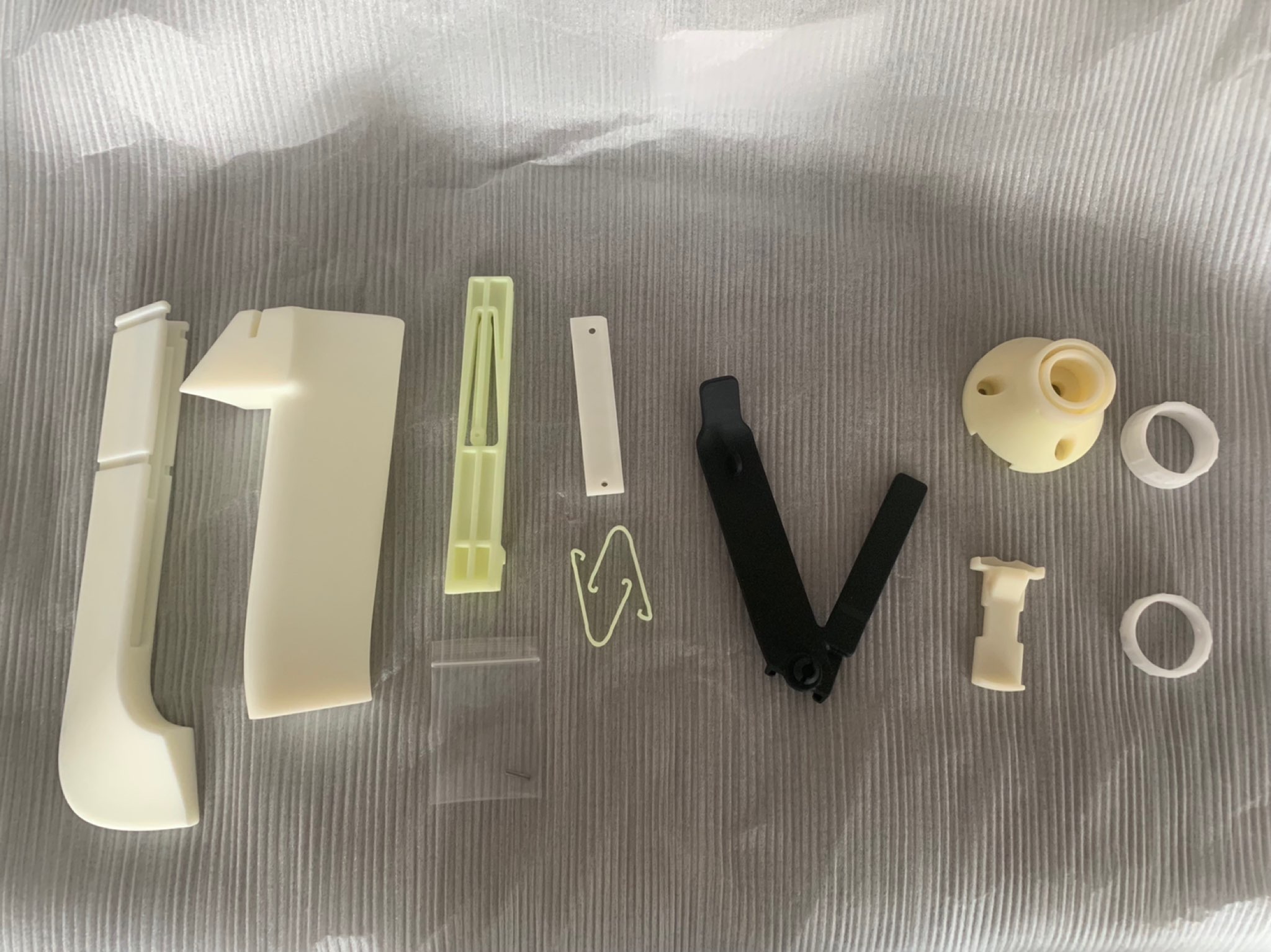


he correct material selection is crucial for creating custom prototypes and parts with the desired mechanical performance, functionality, and aesthetics. At Xiamen Richeng, we offer basic knowledge of 3D printing materials and help you choose the appropriate material for your final part.
SLA
Stereolithography (SLA) is a 3D printing technology that uses photosensitive resin and a laser to create high-precision, detailed parts. The process involves curing a layer of liquid resin with a laser beam, which solidifies the resin and adheres it to the previous layer. The build platform is lowered as each layer is cured until the entire part is complete.
Advantages:
For concept models, prototypes, and complex designs, SLA can produce parts with complex geometries and excellent surface finish compared to other additive manufacturing processes. The cost is competitive.
Disadvantages:
The strength of the prototype parts may not be as good as those manufactured with engineering-grade resin, so parts made with SLA have limited use in functional testing. Fragile, as designs that require strength are usually made with CNC. CNC has multiple materials to choose from and can select different materials based on strength requirements.
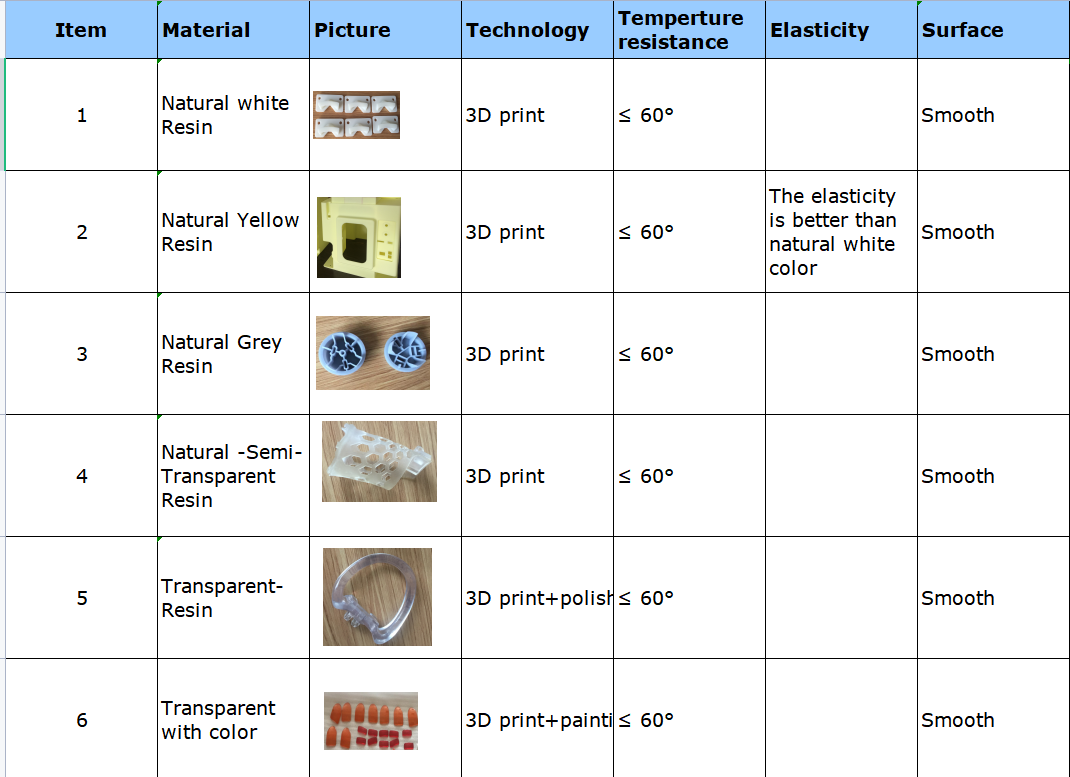
Commonly used materials include:
Godart® 8001 /Godart ®8228 /Godart® 8111X



Actual project we did for reference
SLS
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a 3D printing technology that uses a high-power laser to melt and fuse powdered materials, such as nylon or polyamide, into a solid object. The process involves spreading a thin layer of powdered material over a build platform and then using a laser to selectively sinter (fuse) the powder together in the shape of the desired part. The build platform is lowered as each layer is sintered, and the process is repeated until the entire part is complete. SLS technology is suitable for producing complex geometries and functional parts with high strength. It is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical, for prototyping, tooling, and end-use parts.
Advantages:
SLS nylon has better strength compared to SLA and can process complex structures.
Disadvantages:
The parts have a granular or sandy texture, and the surface is rough, suitable for products with low surface requirements and accuracy.
Commonly used materials include:
PA12
Actual project we did for reference
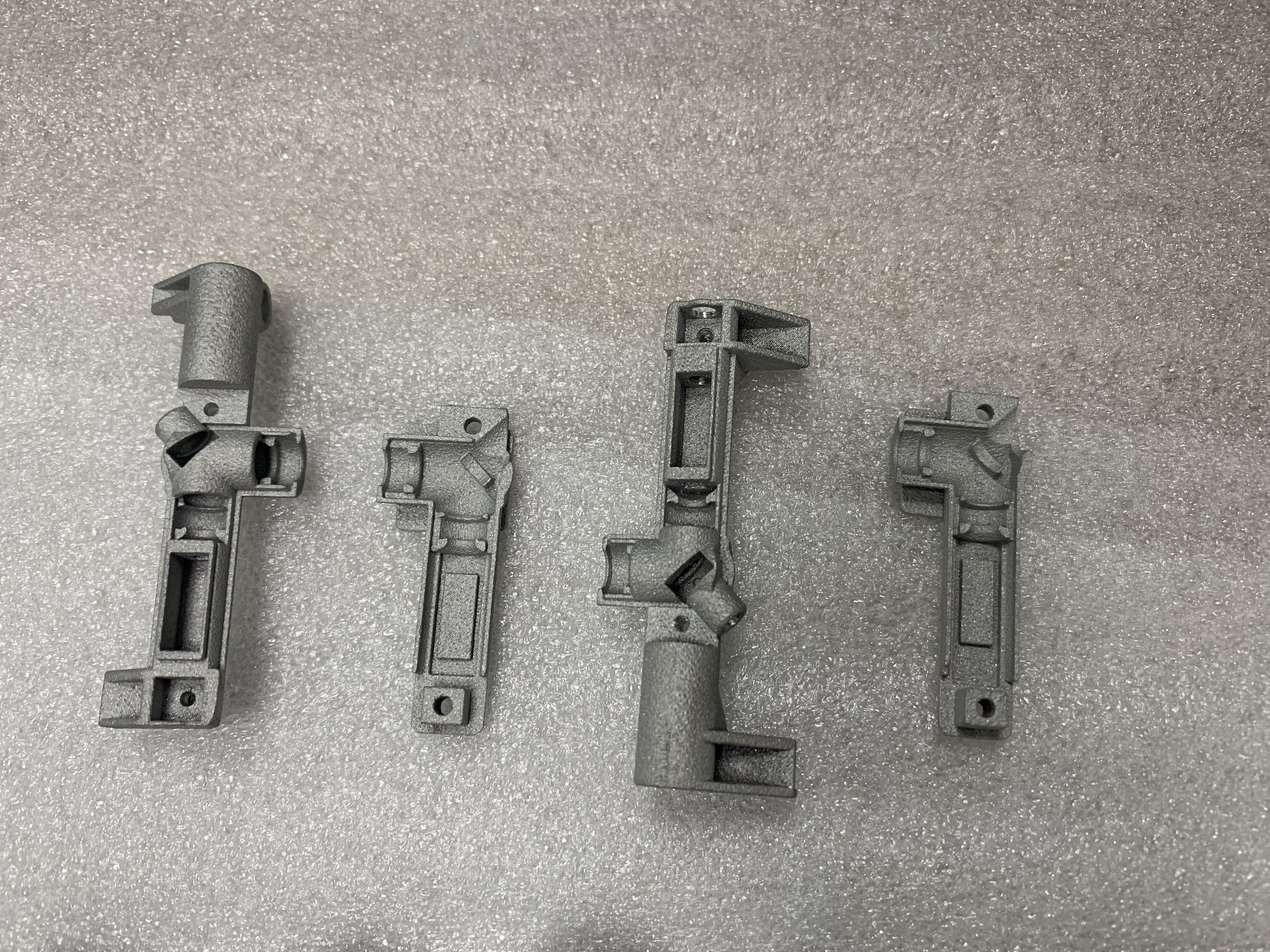
SLM
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is a 3D printing technology that uses a high-power laser to melt and fuse metal powders to create solid parts.
Advantages:
Multiple metals are available for selection and can achieve complex shapes or internal features. Short production time.
Disadvantages:
Compared to SLA/SLS, the price is relatively high, the surface is rough, and a lot of post-processing is required, and the accuracy is not high.
Commonly used materials include:
A1Si10Mg /316L /1.2709 / TC4 /GH4169
Actual project we did for reference

More questions on the 3D printings technology ,please feel free to contact with us .
Post time: Jun-19-2023
